Published: 23/09/21 14:28 Categories: Microbiology
World Sepsis Day will be held this year on September 13th. This clinical syndrome affects 50 million people annually and causes one death every 2.8 seconds.
It is vitally important to acknowledge the impact of sepsis on public health and the use of related resources since the usual care and traditional structures are not adequate for treating affected patients.
What is sepsis?
Sepsis occurs when the body's response to an infection damages its own tissues and organs, i.e. SIRS, and also it is characterized by the presence microorganisms, usually bacteria or fungi. For this reason, it is the last most common cause of death from infectious diseases, including viral infections such as COVID-19.
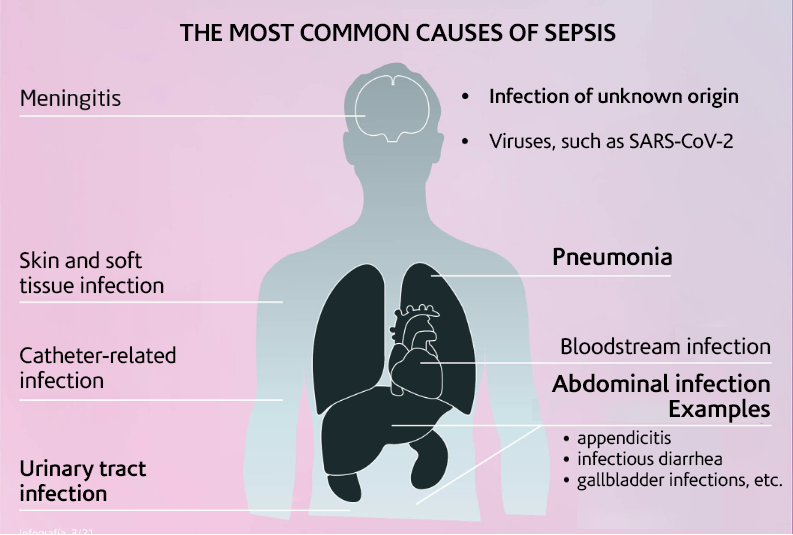
Word Sepsis Day Infographics. Infographic 3 - The most common causes of sepsis. www.worldsepsisday.org/toolkits
The main health complications, including systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), sepsis, severe sepsis, septic shock, multiple organ dysfunction (MODS) and death, may vary in severity levels. The onset of MODS increases the risk of mortality.
The early detection of septic patients allows for interventions such as rapid treatment with antibiotics, resuscitation, and activated protein C.
For the diagnosis, it is important to take samples prior to the antibiotic treatment from both the patient's blood and relevant infected areas in order to prepare culture media, especially blood cultures.
One of the main clinical manifestations of bacteremia and fungemia is sepsis. Therefore, the infection is usually associated and mistakenly confused with the clinical syndrome.
However, it is important to note that sepsis is not always caused by one of these infections, which do not always lead to sepsis. That is, the inadequate treatment of bacteremia or fungemia may lead to this syndrome related to a continuous inflammatory process with alterations in the inflammatory and coagulant responses.
The importance of clinical microbiology
Regarding sepsis, the correct identification of isolates and the portal of entry is essential. Therefore, molecular biology techniques are currently being explored to shorten the times for identifying pathogens.
However, blood culture is still a reference in the diagnosis of sepsis as it is based on the detection of viable microorganisms in blood, allowing for the antimicrobial susceptibility assessment of detected viable pathogens, which is not possible with other techniques.
Current procedures recommend the collection of 2 or 3 blood cultures of 20-30 ml evenly distributed in aerobic and anaerobic bottles. For this purpose, Condalab has available:
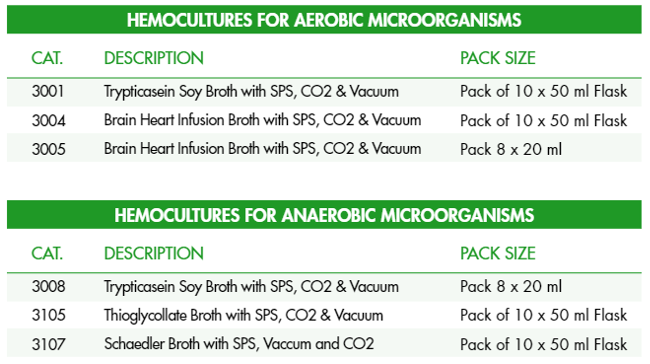
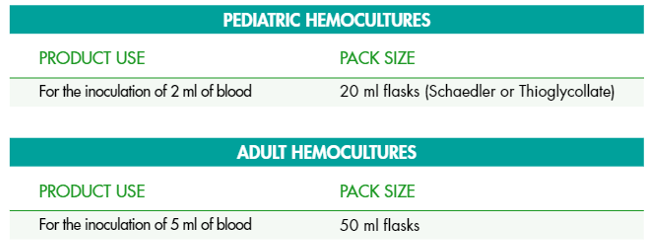
Do not hesitate to contact us for further information about our products, we will be happy to help you.

 Probiotics: Which ones are good?
Probiotics: Which ones are good?
 Condalab Says YES to the World’s Leading Lab Trade Fair: Analytica 2026
Condalab Says YES to the World’s Leading Lab Trade Fair: Analytica 2026
 CONDALAB to Exhibit at WHX Labs Dubai 2026
CONDALAB to Exhibit at WHX Labs Dubai 2026
 Food fraud: How do we detect it?
Food fraud: How do we detect it?
 Visit Us at MEDICA 2025 – Discover Our Precise Detection Solutions
Visit Us at MEDICA 2025 – Discover Our Precise Detection Solutions