Published: 21/11/22 13:37 Categories: Microbiology
Currently clean rooms are a key element in many production and research processes. In recent years, the number of these facilities has increased considerably beyond the hospital setting in places such as pharmaceutical laboratories, assisted reproduction laboratories, and blood and tissue banks.
Clean rooms are the industry´s big ally
The term is defined in UNE EN ISO 171340 as a “room with specific structures and facilities to control contamination and appropriate environmental parameters.” On the other hand, it is common to see other similar terminology such as “clean controlled environments.” The latter are defined in UNE-EN 17141:2021 as a “defined zone in which microbiological contamination is controlled by specific means,” which in turn encompasses the concept of clean room.
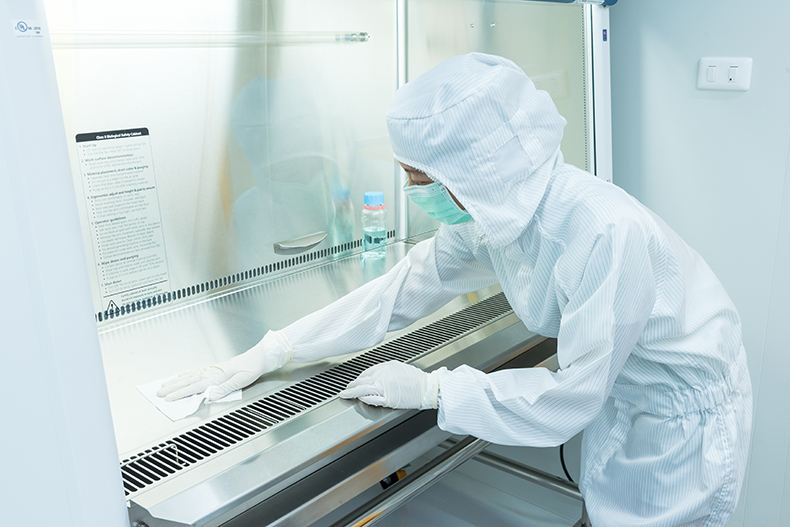

The control of aseptic conditions is essential in this type of facility
In short, a white or clean room is an area designed to work under aseptic conditions and prevent contamination of sterile materials, components and aseptic surfaces.
A large number of parameters such as particle concentration in the air, temperature, humidity, pressure, etc. are monitored in these installations to create an optimal working environment that minimizes the risk of contamination.
Microbiological control of clean rooms
All clean room facilities must implement an environmental control plan, which allows the risk of microbiological contamination to be assessed and controlled, and ensures the effectiveness of the hygiene and safety measures implemented.
Its microbiological control is essentially based on two controls: air control and surface control.
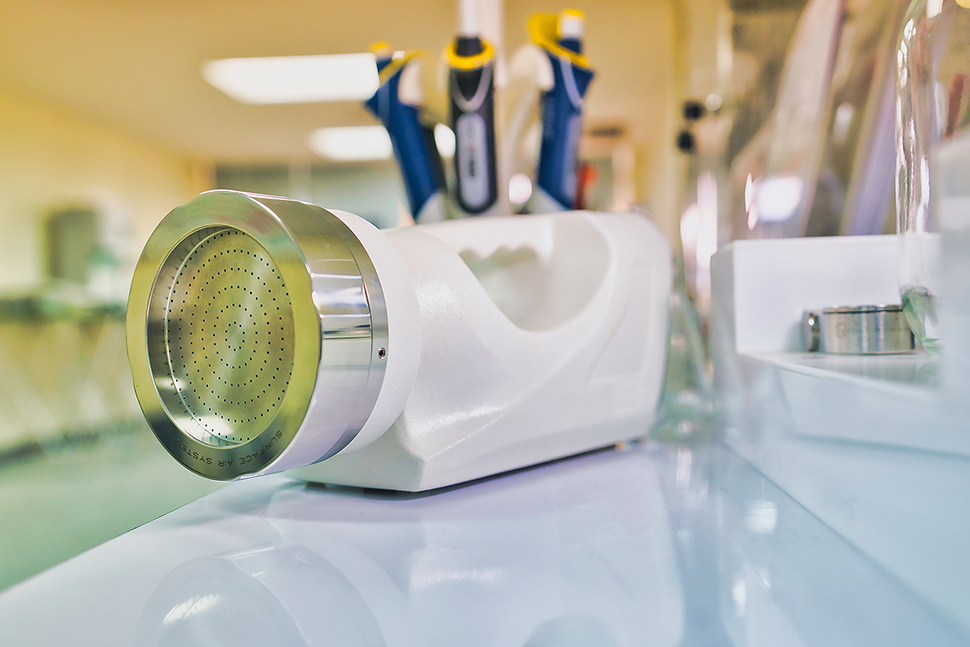

Microbiology air-quality control equipment
For air control, there are mechanical air sampling systems, which suck up constant volumes of air for a given time. Petri dishes 90 mm in diameter are installed in these systems to collect the particles that have been aspirated. Meanwhile, in places where it is difficult to obtain access or space is limited, dish sedimentation is implemented. This method consists of exposing a petri dish to the air for a certain period (1—4 hours) in which those particles that are suspended in the air, and that have been precipitating on the surface of the agar are collected on the dish.
Condalab introduces the new Lateral Code (LC) range, consisting of lateral labeled sedimentation plates, specially designed for microbiological control in the pharmaceutical industry.
The other fundamental microbiological control in clean rooms is surface control. For this type of sampling, Standard UNE-EN 17141:2021 recommends the use of Rodac-type contact plates. These plates have a smaller diameter (55 mm) than petri dishes for sedimentation.
A typical problem in surface sampling is the opening of Rodac plates after use, causing contamination and altering sampling results.
However, at Condalab we have the solution to this problem. The new Lock&Block plates contain a sophisticated locking system that allows plates to be closed and locked after sampling for safe transport to the laboratory where they will be incubated and analyzed. In addition, the locking system has an incubating position, which allows gas exchange for proper aerobic incubation.
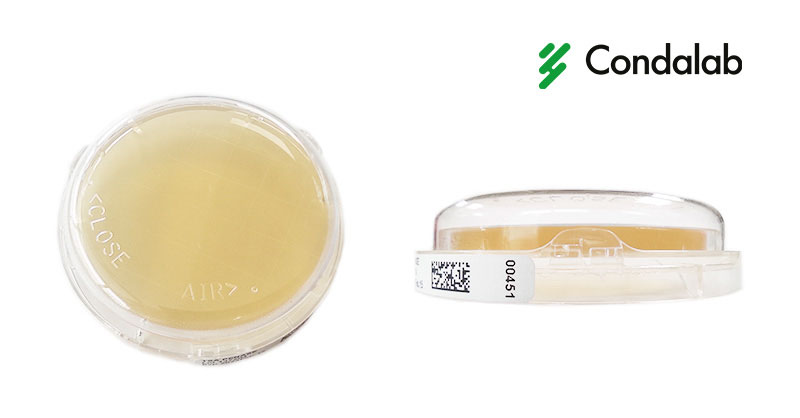
New Lock&Block plates
If you are keen to know more about our Lateral Code and Lock&Block plates, you can find all the information about the range on our website.

 Condalab Says YES to the World’s Leading Lab Trade Fair: Analytica 2026
Condalab Says YES to the World’s Leading Lab Trade Fair: Analytica 2026
 CONDALAB to Exhibit at WHX Labs Dubai 2026
CONDALAB to Exhibit at WHX Labs Dubai 2026
 Food fraud: How do we detect it?
Food fraud: How do we detect it?
 Visit Us at MEDICA 2025 – Discover Our Precise Detection Solutions
Visit Us at MEDICA 2025 – Discover Our Precise Detection Solutions
 PCR: The Technique Revolutionizing Rapid Detection in the Food Industry
PCR: The Technique Revolutionizing Rapid Detection in the Food Industry