Published: 24/03/21 16:43 Categories: Microbiology
We regularly consume eyedrops, injectables, and products that must meet the condition of being sterile, but how is this achieved? This characteristic is critical for a pharmaceutical product and must be ensured through a properly designed and validated manufacturing process.

Product sterility is achieved by controlling the bioburden and by using an adequate aseptic technique for the processing. In this sense, the European Pharmacopoeia recommends the Sterility Test to verify if a product complies with this requirement.
How is a Sterility Test performed?
Some necessary tests must be previously carried out. The first one is the Growth Promotion Test, which aims to certify that the culture media have the capacity to promote the growth of very low levels of microorganisms. At the same time, the nutritional properties of each medium batch to be used are confirmed.
For this purpose, less than 100 CFU of each species stated in the Ph. Eur. must be inoculated in Thioglycollate Fluid Medium (TFM) and Trypticasein Soy Broth (TSB), and also in TSA/SDA as a positive control. Once the incubation is over, the medium is suitable if growth is clearly observed.
The second requirement is the Method Suitability Test, which is carried out simultaneously with the previous test to demonstrate that the method is adequate to control the product sterility.
The same methods as in the Sterility Test (membrane filtration or direct transfer) are used but the difference is that the product is transferred to each medium, TFM/TSB, and then inoculated with less than 100 CFU of each species.
After incubation, in a visual comparison with a blank (no product), the test is suitable for the product if visible growth is observed. Otherwise, the product possesses antimicrobial activity.
Having mentioned the above, the Sterility Test must be carried out under aseptic conditions and, as indicated, by membrane filtration or direct transfer. The minimum and maximum volumes of the product are stated in the Ph. Eur., as well as the method to be used that depends on the products’ nature:
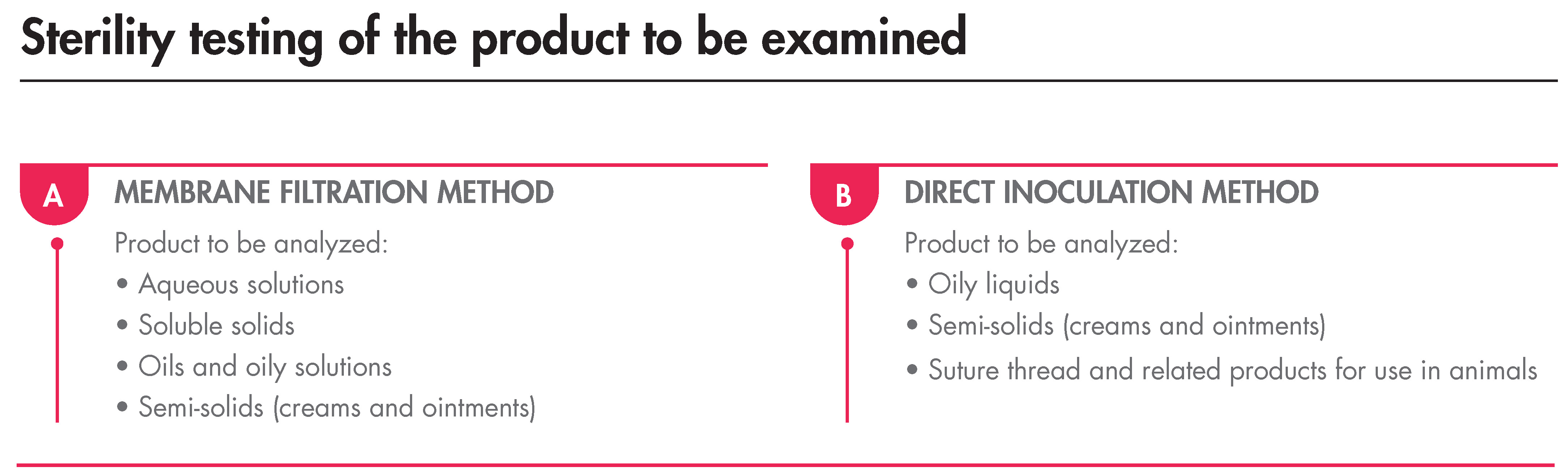
The incubation, regardless of the method, must last for 14 days and, after this time, if no turbidity is observed, the product complies with the test.
Only two culture media are necessary?
Both the TFM and the TSB are general media with highly nutritious characteristics that allow the growth of a wide variety of bacteria (aerobes and anaerobes) and fungi at very low levels since, under the premise of sterility, a considerable number of microorganisms that may contaminate the product should not be found.
In addition, this method is harmonized with the USP and JP, which is a significant additional advantage.
In Condalab we have available media according to pharmacopoeia to perform the Sterility Test without complications as each batch is assessed to comply with high-quality standards to ensure their sterility and performance.
For further information about this topic, catch our CondalabTalk The Sterility Test and Media Fill Testing. Register to watch the recording!

 Food fraud: How do we detect it?
Food fraud: How do we detect it?
 Visit Us at MEDICA 2025 – Discover Our Precise Detection Solutions
Visit Us at MEDICA 2025 – Discover Our Precise Detection Solutions
 PCR: The Technique Revolutionizing Rapid Detection in the Food Industry
PCR: The Technique Revolutionizing Rapid Detection in the Food Industry
 How Culture Media Ensure the Safety, Efficacy, and Quality of Medicines
How Culture Media Ensure the Safety, Efficacy, and Quality of Medicines
 Meeting us at MEDLAB MIDDLE EAST 2025
Meeting us at MEDLAB MIDDLE EAST 2025